卫星平台信息安全 bus 构建challenge镜像
1 docker build challenge -t bus:challenge
然后
1 socat -v tcp-listen:31340,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} bus\:challenge"
后面就能通过nc与31340端口交互
题目告诉我们,正在监听的总线非常繁忙,一些有趣的信息隐藏在总线设备内存中。
连接上题目后,发现回显了下面一大串字符,以NO CARRIER结尾
1 2 3 4 ^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+12+47+40+41+c6+97+e1+3f+89+81+3f+c1+99+1d+a1+c0+20+18+a1+40+5e+42+ac+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+20+fa+3f+41+c8+da+e2+3f+a6+64+3f+c1+ff+33+a1+c0+a4+d2+a0+40+de+50+55+40+.^b4+01+c9+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+e6+8f+3c+ba+5b+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+80+2e+42+57+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1d+ec+3f+41+d8+04+e5+3f+67+4e+40+c1+38+1b+a1+c0+e1+dd+a0+40+b9+91+91+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1d+ec+3f+41+d8+04+e5+3f+67+4e+40+c1+38+1b+a1+c0+e1+dd+a0+40+b9+91+91+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+da+81+3f+41+50+c7+e3+3f+9c+28+40+c1+77+df+a0+c0+44+1d+a0+40+7f+b7+52+40+.^b4+01+7e+5f+9a+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+32+00+90+2e+f3+7b+07+99+eb+9b+43+16+a2+b1+9a+a0+2d+f9+3a+72+f7+8f+cb+d7+e3+80+43+1d+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+41+85+40+41+e2+7a+e1+3f+e8+28+40+c1+fc+50+a0+c0+6e+09+9f+40+57+8c+e9+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+41+85+40+41+e2+7a+e1+3f+e8+28+40+c1+fc+50+a0+c0+6e+09+9f+40+57+8c+e9+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+ce+79+3f+41+5e+35+e6+3f+5d+a7+3f+c1+4c+81+a0+c0+57+75+9f+40+0b+f3+50+40+.^b4+01+93+99+eb+9b+43+16+a2+b1+9a+a0+2d+f9+3a+72+f7+8f+cb+d7+e3+80+43+1d+12+94+c7+59+78+58+87+6b+d3+8e+04+be+2a+47+d4+cc+f8+6e+6c+26+67+a6+98+5e+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+e8+7f+40+41+bf+c7+e1+3f+3c+f0+3f+c1+1a+02+9f+c0+9f+ff+9e+40+a8+59+d3+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+e8+7f+40+41+bf+c7+e1+3f+3c+f0+3f+c1+1a+02+9f+c0+9f+ff+9e+40+a8+59+d3+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+49+bc+3f+41+0e+cc+e2+3f+4f+8d+40+c1+a4+81+9f+c0+5c+29+a1+40+ea+53+51+40+.^b4+01+9f+72+f7+8f+cb+d7+e3+80+43+1d+12+94+c7+59+78+58+87+6b+d3+8e+04+be+2a+47+d4+cc+f8+6e+6c+26+67+a6+98+5e+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+ff+82+3f+41+e6+d3+e2+3f+51+e5+3f+c1+84+93+a0+c0+89+72+a0+40+bb+a8+9e+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+ff+82+3f+41+e6+d3+e2+3f+51+e5+3f+c1+84+93+a0+c0+89+72+a0+40+bb+a8+9e+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+e7+83+40+41+cc+ef+e7+3f+e0+b3+3f+c1+a1+e0+9e+c0+f7+5c+a0+40+08+b6+53+40+.^b4+00+25+7b+91+82+23+fc+65+a6+3a+b0+a1+55+53+eb+5b+d1+8f+be+17+81+cb+6f+35+b6+bf+9e+85+4a+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+0b+82+3f+41+75+42+e2+3f+1b+7c+3f+c1+b0+c1+a0+c0+4d+c0+9e+40+53+22+b2+bc+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+0b+82+3f+41+75+42+e2+3f+1b+7c+3f+c1+b0+c1+a0+c0+4d+c0+9e+40+53+22+b2+bc+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+9c+95+40+41+7e+fc+e8+3f+a3+37+40+c1+cc+78+9f+c0+78+d0+9e+40+8e+fd+51+40+.^b4+01+6e+92+e6+e7+10+ea+d8+a5+70+94+aa+2b+06+6e+84+fe+7c+5f+9a+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+32+00+90+2e+f3+7b+07+99+eb+9b+43+16+a2+b1+9a+a0+2d+f9+3a+72+f7+8f+cb+d7+e3+80+43+1d+12+94+c7+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1c+f0+3f+41+6b+5b+e7+3f+8b+78+3f+c1+e3+97+a0+c0+3d+c1+a0+40+b9+f2+d3+bc+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1c+f0+3f+41+6b+5b+e7+3f+8b+78+3f+c1+e3+97+a0+c0+3d+c1+a0+40+b9+f2+d3+bc+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+4a+69+3f+41+05+fb+e9+3f+9d+1b+40+c1+8f+05+a0+c0+a7+08+a0+40+f8+28+51+40+.^b4+00+cf+28+65+f5+e6+8f+3c+ba+5b+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+80+2e+42+57+1e+6a+bc+13+50+4b+50+0a+a6+85+32+6d+e0+c2+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+46+6c+3f+41+b4+83+e5+3f+32+70+3f+c1+b1+30+a0+c0+d9+d3+a0+40+d9+e9+e1+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+46+6c+3f+41+b4+83+e5+3f+32+70+3f+c1+b1+30+a0+c0+d9+d3+a0+40+d9+e9+e1+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+a3+02+40+41+16+a4+e4+3f+ae+6f+40+c1+6e+58+a0+c0+1b+3d+9f+40+b4+be+54+40+.^b4+00+d7+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+80+2e+42+57+1e+6a+bc+13+50+4b+50+0a+a6+85+32+6d+e0+c2+da+d3+b0+7c+2b+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+9d+8b+3f+41+9f+f0+e8+3f+87+99+3f+c1+e2+e3+9f+c0+0d+a5+9f+40+9c+cb+f6+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+9d+8b+3f+41+9f+f0+e8+3f+87+99+3f+c1+e2+e3+9f+c0+0d+a5+9f+40+9c+cb+f6+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+69+fb+3f+41+cd+f3+e5+3f+1e+6b+3f+c1+51+cc+9e+c0+83+0f+a1+40+53+bb+55+40+.^b4+01+c8+74+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+e6+8f+3c+ba+5b+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+14+10+40+41+6d+51+eb+3f+1e+e0+3f+c1+14+39+9f+c0+8a+1f+a0+40+f1+d5+f6+bc+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+14+10+40+41+6d+51+eb+3f+1e+e0+3f+c1+14+39+9f+c0+8a+1f+a0+40+f1+d5+f6+bc+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+93+ab+3f+41+d0+e1+e8+3f+9b+7a+3f+c1+5c+dc+9e+c0+d6+bd+9f+40+b5+21+55+40+.^b4+00+4e+d7+ac+75+32+7e+04+f1+95+85+bc+04+bb+72+c4+59+f7+0e+db+9c+c8+9e+bb+14+e2+fe+5b+8c+e6+dd+e5+70+b5+92+e6+e7+10+ea+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+0e+a7+3f+41+ce+3c+e4+3f+81+5e+40+c1+ab+9d+9f+c0+16+e4+9e+40+be+5a+73+3c+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+0e+a7+3f+41+ce+3c+e4+3f+81+5e+40+c1+ab+9d+9f+c0+16+e4+9e+40+be+5a+73+3c+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+93+32+40+41+cb+04+e6+3f+0f+c1+3f+c1+92+50+a0+c0+60+3f+9f+40+7c+25+54+40+.^b4+00+a5+80+43+1d+12+94+c7+59+78+58+87+6b+d3+8e+04+be+2a+47+d4+cc+f8+6e+6c+26+67+a6+98+5e+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+e6+8f+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+f6+69+40+41+f6+a2+e1+3f+7c+8b+40+c1+a4+c9+9f+c0+90+10+a0+40+71+57+1d+bd+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+f6+69+40+41+f6+a2+e1+3f+7c+8b+40+c1+a4+c9+9f+c0+90+10+a0+40+71+57+1d+bd+.^83+00+00+3f+.^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+87+03+40+41+2e+20+e3+3f+48+64+40+c1+09+cc+9f+c0+f8+27+a1+40+63+89+53+40+.^b4+00+31+eb+5b+d1+8f+be+17+81+cb+6f+35+b6+bf+9e+85+4a+4a+75+69+63+79+20+44+61+74+61+20+30+31+00+d7+ac+75+32+7e+04+.^83+00+00+1f+.^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+a3+11+40+41+4d+35+e8+3f+d3+94+40+c1+82+60+9f+c0+ea+cf+a0+40+4e+4f+04+3d+. +++ NO CARRIER
根据题目描述,回显的字符串应该是某种总线协议数据,需要参赛者识别是哪种总线协议并对其进行解析,按照协议格式提交请求,以获取隐藏的信息。
背景知识
$I^2C$(Inter-Integrated Circuit,集成电路总线)是一种串行通信总线,使用多主从架构,由飞利浦公司在20世纪80年代为了使用主板,嵌入式系统或手机连接低速周边设备而研发。
$I^2C$仅使用两条线在连接到总线的设备间传送信息,其中一条线为串行数据线(SDA),另一条线为串行时钟线(SCL)。总线上的每个设备都有唯一的地址区分。通常$I^2C$在硬件设计中作为传感器接口和EEPROM存储器的接口使用。
基础信号
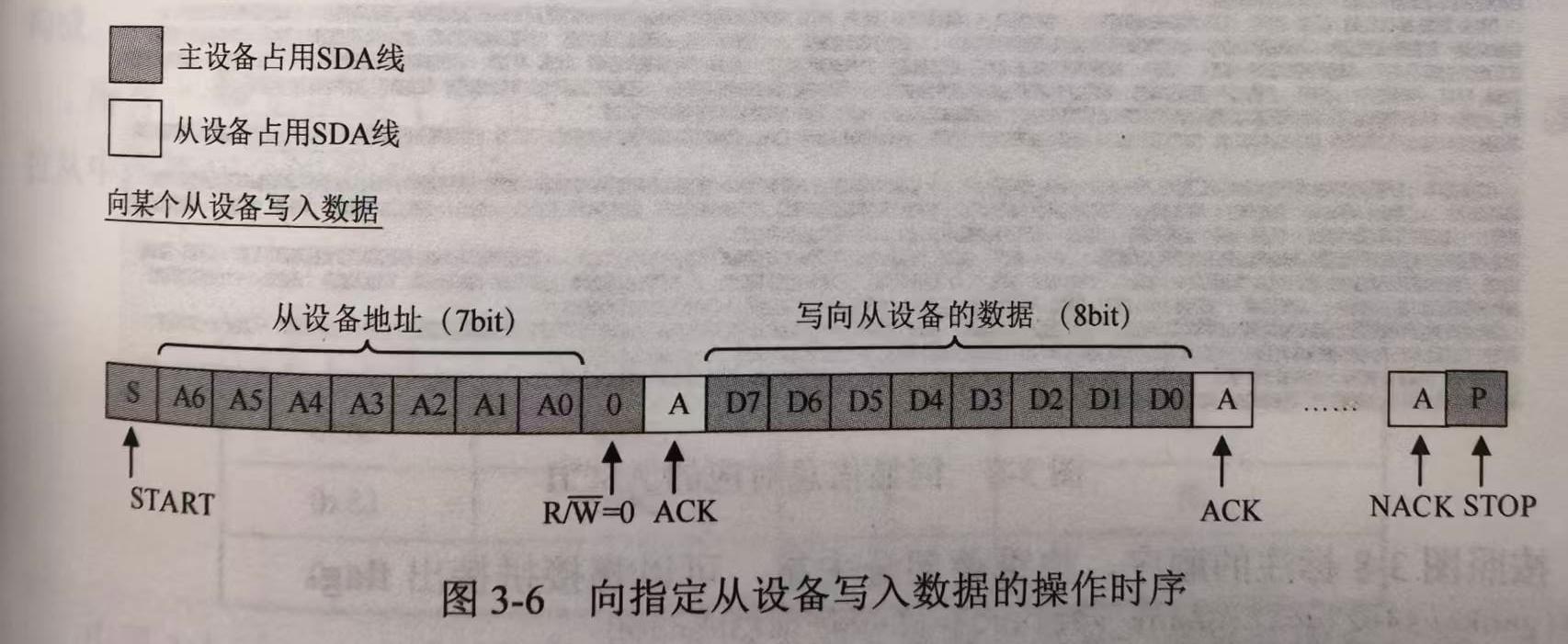
START信号和STOP信号均由主设备产生。所有信息传输都从START信号开始,以STOP信号结束。START信号和STOP信号之间的阶段认为$I^2C$总线处于忙碌(busy)状态。
$I^2C$有完善的应答机制,每个字节后面必须跟一个ACK信号或NAK信号。
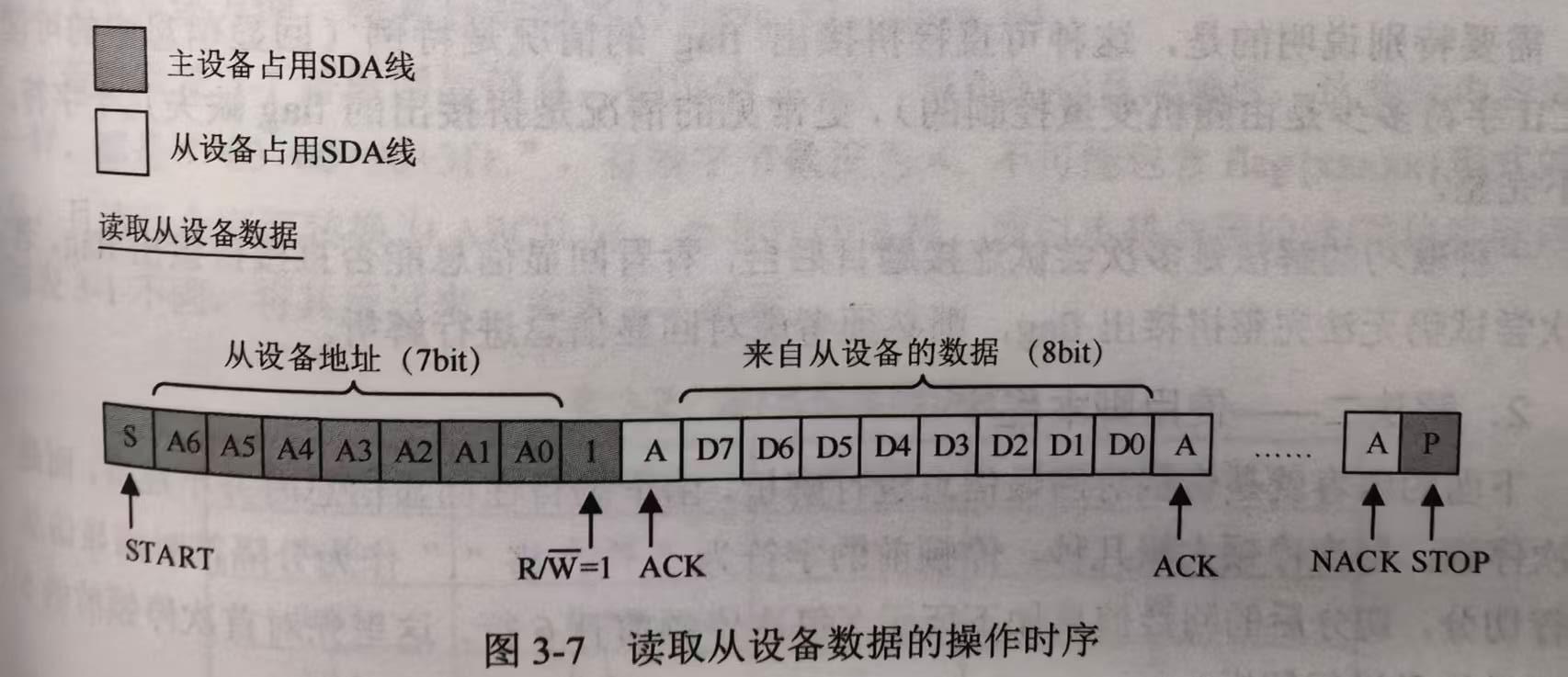
读/写时序
可以发现回显的信息是以 ^ 和 . 两种字符分割的,每行都是以 ^ 开始,以 . 结束的,因此 ^ 和 . 应该是控制字符。通过搜索卫星总线常用的总线协议的报文格式,初步判断上述字符串最有可能为$I^2C$协议。下面尝试按$I^2C$来解析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+12+47+40+41+c6+97+e1+3f+89+81+3f+c1+99+1d+a1+c0+20+18+a1+40+5e+42+ac+3c+. ^83+00+00+3f+. ^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+20+fa+3f+41+c8+da+e2+3f+a6+64+3f+c1+ff+33+a1+c0+a4+d2+a0+40+de+50+55+40+. ^b4+01+c9+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+e6+8f+3c+ba+5b+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+80+2e+42+57+. ^83+00+00+1f+. ^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1d+ec+3f+41+d8+04+e5+3f+67+4e+40+c1+38+1b+a1+c0+e1+dd+a0+40+b9+91+91+3c+. .....(省略)
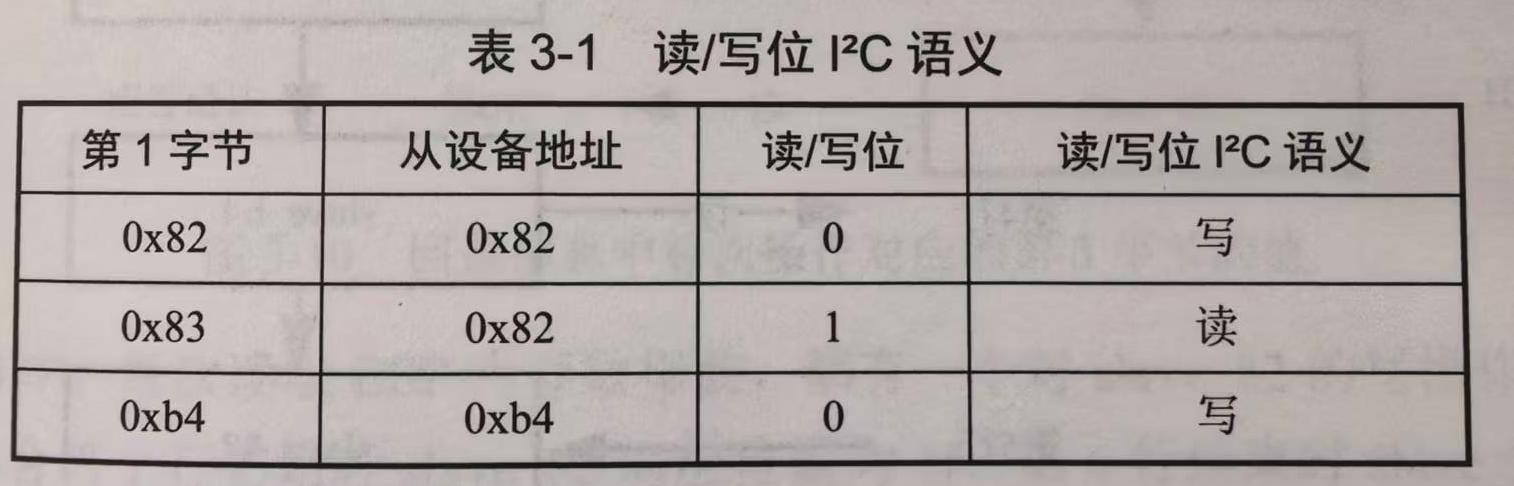
若是$I^2C$协议,由上文的背景知识可知,^ 为$I^2C$总线START信号,. 为$I^2C$总线STOP信号。^ 后面的1字节由7bit从设备地址和最低位的1bit读/写位构成。
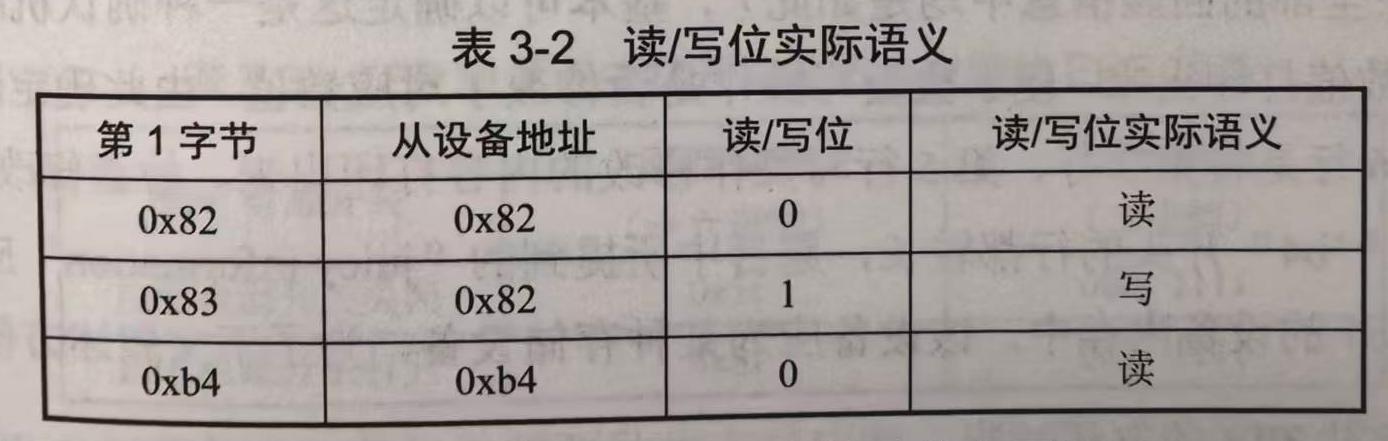
所有 ^ 后的第1字节只有 0x82,0x83,0xb4 3种,将从设备地址和1bit读/写位从中剥离开,如下表所示。
由上表可知,本题的$I^2C$总线上仅有两种从设备,地址分别为0x82和0xb4,为方便,将其分别命名为slave_82,slave_b4。
若按照上表解析回显信息,则仅由 ^83 开头的行是读操作,这些行的内容仅有 ^83+00+00+3f+. 和 ^83+00+00+1f+. 两种,有效字节数仅为4,不可能包含flag{xxxxx}形式的信息。并且这几个字符转换为ASCII后,是非打印字符。因此本题的读/写位实际语义与上表不同,将其反过来,如下表所示。
按照上表的语义解析回显信息,各行完成的功能如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 // 从slave_82读取数据 ^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+12+47+40+41+c6+97+e1+3f+89+81+3f+c1+99+1d+a1+c0+20+18+a1+40+5e+42+ac+3c+. // 向slave_82写入数据 ^83+00+00+3f+. // 从slave_82读取数据 ^82+00+00+3f+00+00+00+20+fa+3f+41+c8+da+e2+3f+a6+64+3f+c1+ff+33+a1+c0+a4+d2+a0+40+de+50+55+40+. // 从slave_b4读取数据 ^b4+01+c9+61+20+30+33+00+f0+28+65+f5+e6+8f+3c+ba+5b+35+28+c7+5b+8f+6d+f3+ee+a2+57+23+bb+3b+9c+f0+31+a9+ed+80+2e+42+57+. // 向slave_82写入数据 ^83+00+00+1f+. // 从slave_82读取数据 ^82+00+00+1f+00+00+00+1d+ec+3f+41+d8+04+e5+3f+67+4e+40+c1+38+1b+a1+c0+e1+dd+a0+40+b9+91+91+3c+. .....(省略)
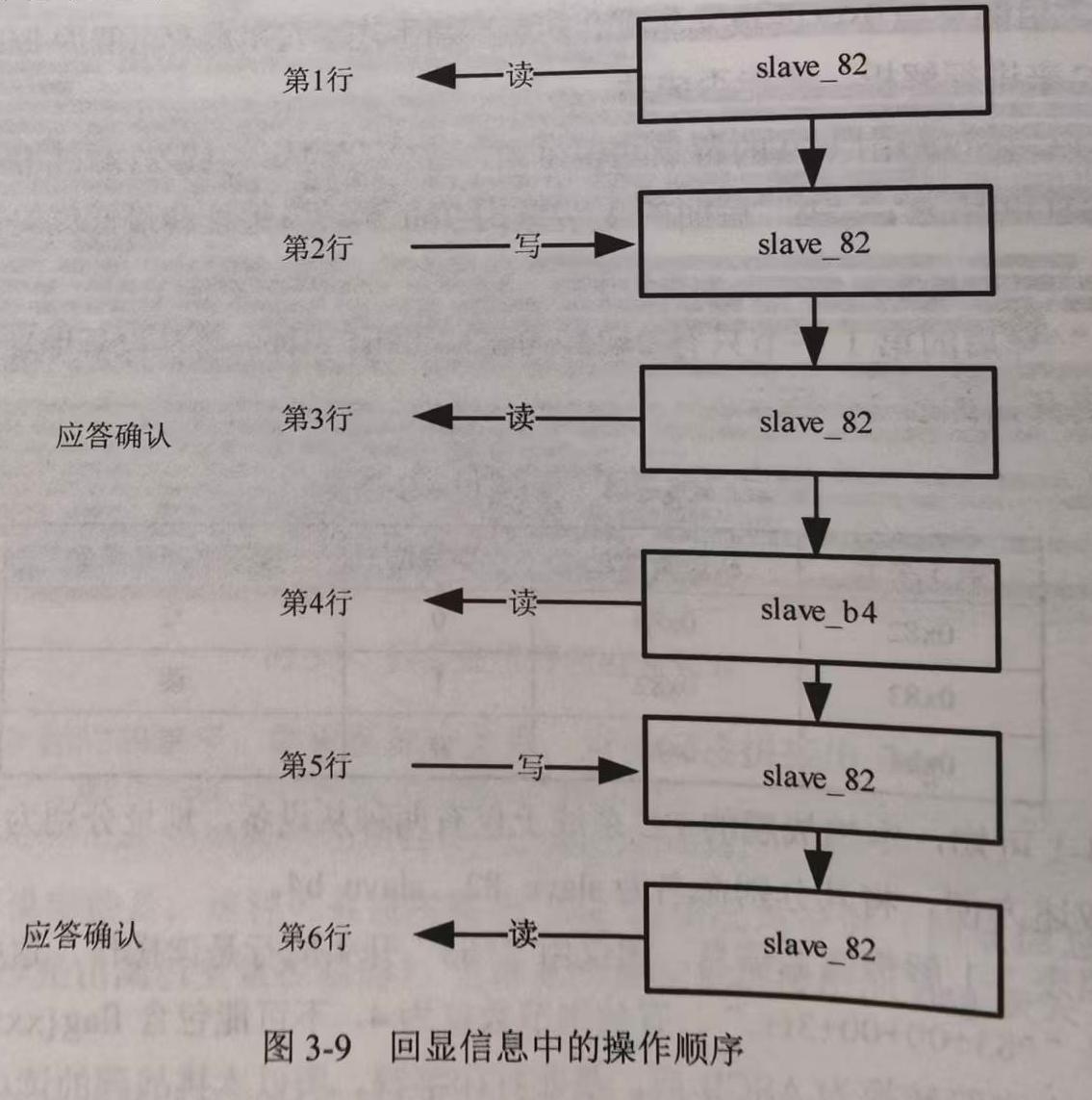
为便于理解,将上面的操作顺序绘制成图,如下图所示。
上图中,每次写操作后都紧跟着一个针对同样地址的读操作(不仅这里分析的前6行如此,在全部的回显信息种都是如此),基本可以确定这是一种确认机制,读操作将修改后的数值打印出来,便于检查写操作是否修改了对应数值。
此外,可以发现所有以 ^b4 开头的行都较长,题目的flag可能就藏在地址为0xb4是设备内存中,该设备应为某种存储设备,后面为方便将其命名为EEP。
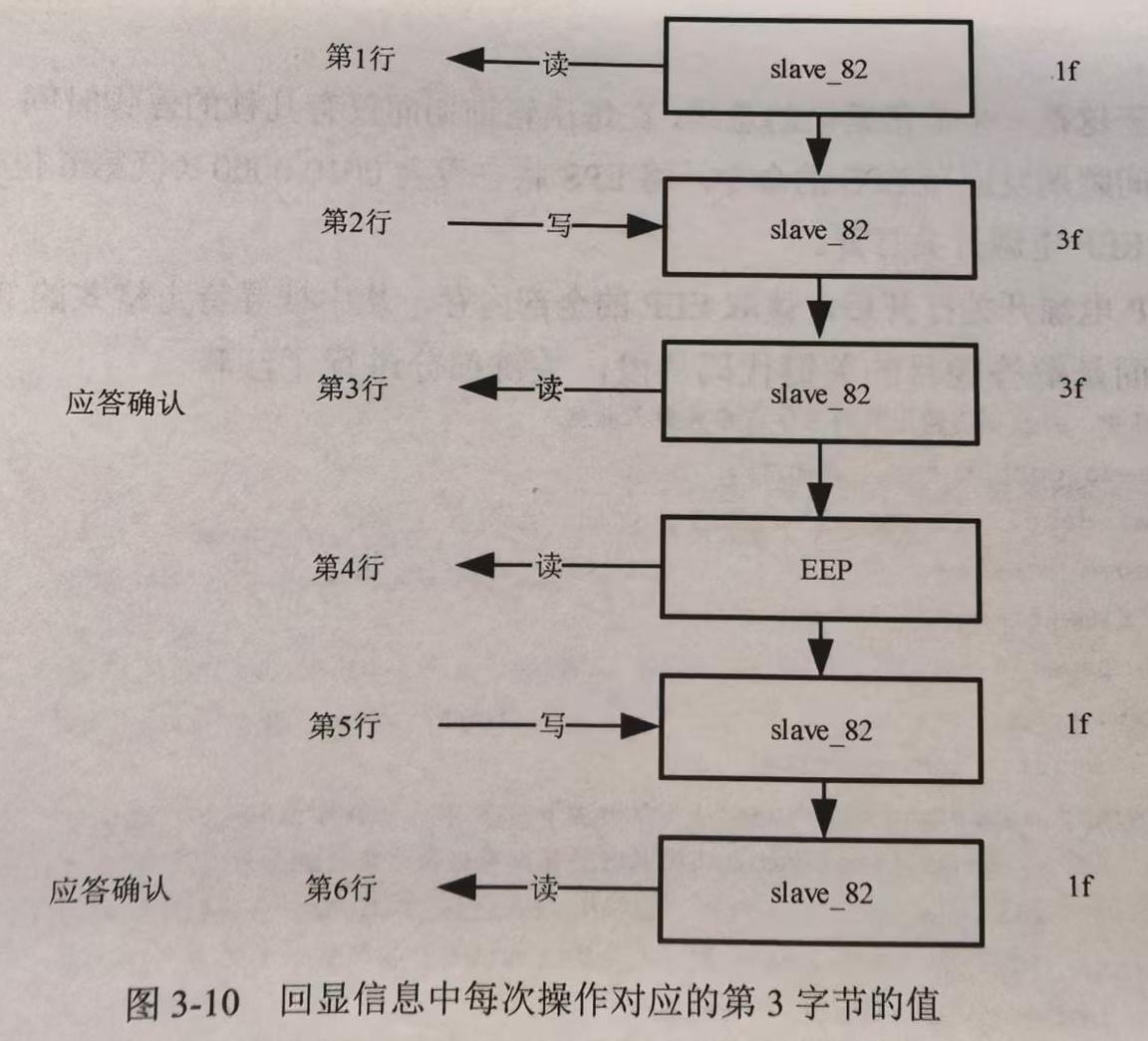
写操作对应行为 ^83+00+00+3f+. ,由$I^2C$的背景知识可知,”00 00 3f”为写入的内容。与对应的读操作行相应位置内容比较,由写操作的”00 00 3f”变为读操作的”00 00 1f”,变化的仅有第3字节,且前2字节始终为0,所以下面只对第3字节进行分析,如下图所示。
上图中,每次读取EEP内存数据前,都有一个对slave_82的写操作(写入内容为3f),结合第1行初始时slave_82对应位置为1f,第6行结束时slave_82对应位置也为1f,可以总结出如下的操作步骤。
每次读取EEP前,都要对slave_82进行写操作。
每次读取EEP后,slave_82都会被再次写入,恢复其初始状态。
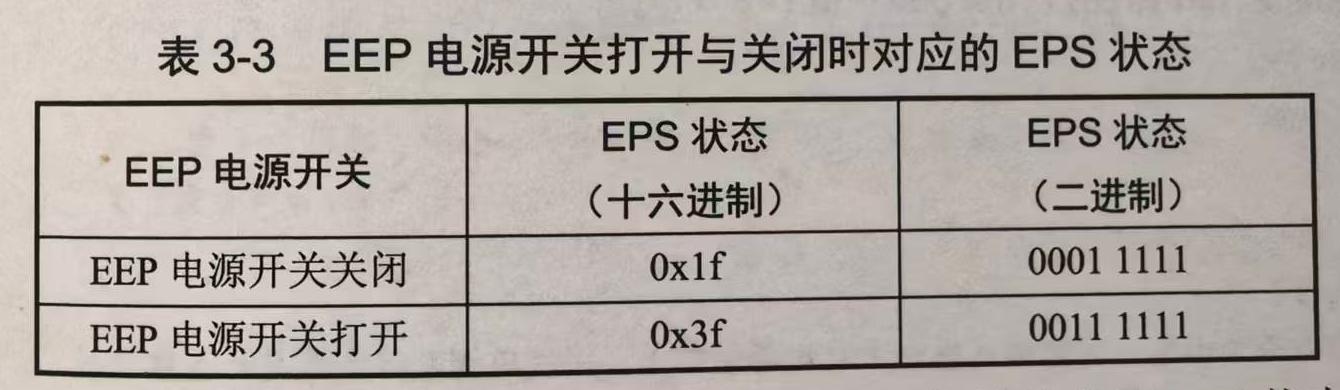
很明显,slave_82控制着EEP的开与关,参考卫星设计的有关文献,猜测slave_82为电源控制系统,将其命名为EPS。EEP电源开关打开与关闭时对应的EPS状态如下表所示。
由EEP电源开关在打开与关闭两种状态对应的二进制形式的EPS状态可知,表示EPS状态(二进制)的第6位(从右向左数)代表EEP。
题目描述说正在监听的总线非常繁忙,也就是说$I^2C$总线在大部分时间被主设备占用,要获取EEP中的数据,就必须将主设备电源开关关闭释放总线,并将EEP电源开关打开。这可以通过将表示EPS状态(二进制)的第6位(从右向左数)置1,其他位置0来实现。
由于这是一个非常繁忙的总线,在每次轮询期间仅有几秒的停顿时间,因此需要利用这个间隙期发送写EPS的命令,将EPS状态设为0010 0000(仅第6位设置为1),即仅将EEP电源开关打开。
EEP电源开关打开后,读取EEP的全部内存,从中搜寻flag即可。
构建solver镜像
1 docker build solver -t bus:solver
测试
1 2 3 socat -v tcp-listen:31340,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} bus\:challenge" docker run -it --rm -e "HOST=172.17.0.1" -e "PORT=31340" bus:solver
地面段信息安全 verizon 构建challenge镜像
1 docker build challenge -t verizon:challenge
然后
1 socat -v tcp-listen:31333,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -p 31336\:8123 -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} -e SERVICE_HOST=10.249.10.107 -e SERVICE_PORT=31336 verizon\:challenge"
后面就能通过nc与31333端口交互
本挑战题的背景是LaunchDotCom地面站正在从Carnac1.0卫星接收遥测数据。本挑战题要求根据XTCE定义实现解码器,从而实现对遥测数据的解码。
使用nc连接到靶机后,显示遥测服务正在发送一系列二进制数据,打印出来是乱码,参赛者需要对此二进制数据,根据XTCE定义实现解码,才可得到flag值。
题目还给出了一个XTCE格式的文件telemetry.xtce。XTCE是描述遥测和命令的数据规范,通过该文件可以解析遥测服务发送的二进制数据的含义。
通过快速查看XTCE文件,可以找到flag是如何定义的,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <!-- Parameters used by FLAG Gen --> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG11"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG12"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG13"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG14"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG15"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG16"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG17"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG18"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG19"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG10"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG1"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG2"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG3"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG4"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG5"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG6"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="7BitInteger" name="FLAG7"/> ...
可以看出每一个flag中的字符都是7位编码的,但是计算机中8位ASCII码表示一个字符,这意味着原始二进制文件中不会看到有意义的flag。
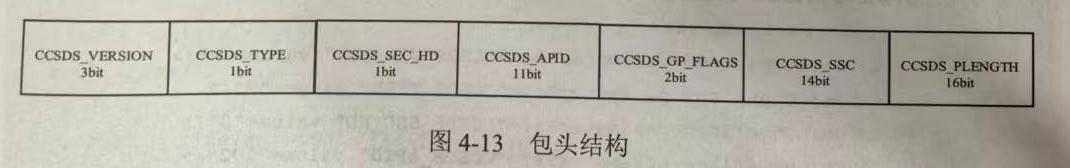
在SequenceContainer中,我们可以看到包的结构。包头结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <xtce:SequenceContainer name="AbstractTM Packet Header" shortDescription="CCSDS TM Packet Header" abstract="true"> <xtce:EntryList> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_VERSION"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_TYPE"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_SEC_HD"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_APID"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_GP_FLAGS"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_SSC"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="CCSDS_PLENGTH"/> </xtce:EntryList>
该部分指定了一个名为AbstractTM Packet Header的容器。注意parameterRef参数,它指向ParameterSet部分先前定义的参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <xtce:ParameterSet> <!-- Parameters used by space packet primary header --> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="3BitInteger" name="CCSDS_VERSION"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="1BitInteger" name="CCSDS_TYPE"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="1BitInteger" name="CCSDS_SEC_HD"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="11BitInteger" name="CCSDS_APID"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="2BitInteger" name="CCSDS_GP_FLAGS"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="14BitInteger" name="CCSDS_SSC"/> <xtce:Parameter parameterTypeRef="2ByteInteger" name="CCSDS_PLENGTH"/>
从这里我们可以得知,包头结构如下图所示:
如果把以上所有的字段加起来,会得到一个6字节长的包头。其中我们观察到CCSDS_APID参数,本题目中APID的含义是应用过程识别符,它能够唯一标识特定类型数据包的类型ID。
查看flag包的格式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 <xtce:SequenceContainer name="AbstractFlag Packet" shortDescription="Flag TM Packet Header" abstract="true"> <xtce:EntryList> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG1"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG2"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG3"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG4"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG5"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG6"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG7"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG8"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG9"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG10"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG11"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG12"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG13"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG14"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG15"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG16"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG17"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG18"/> ...... <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG110"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG111"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG112"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG113"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG114"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG115"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG116"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG117"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG118"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG119"/> <xtce:ParameterRefEntry parameterRef="FLAG120"/> </xtce:EntryList> <xtce:BaseContainer containerRef="AbstractTM Packet Header"> <xtce:RestrictionCriteria> <xtce:ComparisonList> <xtce:Comparison parameterRef="CCSDS_VERSION" value="0"/> <xtce:Comparison parameterRef="CCSDS_TYPE" value="0"/> <xtce:Comparison parameterRef="CCSDS_SEC_HD" value="0"/> <xtce:Comparison parameterRef="CCSDS_APID" value="102"/> </xtce:ComparisonList> </xtce:RestrictionCriteria> </xtce:BaseContainer> </xtce:SequenceContainer> </xtce:ContainerSet> </xtce:TelemetryMetaData> </xtce:SpaceSystem>
我们可以在这里看到一个新的部分-RestrictionCriteria(限制标准)。限制标准是一种匹配条件。该部分告诉我们,解析器应该满足哪些条件才能将内容解析为flag包。也就是说,flag包的包头满足以下条件。
因此,这道题目的解题思路可以分为以下4步:
solve.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import bitstringimport osimport sysimport socketFLAG_APID = 102 EPS_APID = 103 PAYLOAD_APID = 105 if __name__ == '__main__' : Host = '10.249.10.107' Port = 31333 sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect((Host, Port)) ticket = os.getenv("TICKET" , "" ) if len (ticket): sock.recv(128 ) sock.send((ticket + "\n" ).encode("utf-8" )) line = sock.recv(128 ) sock.close() Host, Port = line.split(b" " )[-1 ].split(b":" ) print (Host,Port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect((Host, int (Port))) while True : data = b'' while len (data) < 6 : data += sock.recv(6 - len (data)) s = bitstring.BitArray(data) version, type , sec_header, apid, sequence_flags, sequence_count, data_length = s.unpack('uint:3, uint:1, uint:1, uint:11, uint:2, uint:14, uint:16' ) print ("APID: {}\nLength: {}\n" .format (apid, data_length)) data = b'' while len (data) < data_length+1 : data += sock.recv(data_length+1 - len (data)) if apid != FLAG_APID: print ("Ignoring APID we don't care about" ) continue s = bitstring.ConstBitStream(data) char = ' ' flag = '' while char != '}' : char = chr (s.read('uint:7' )) flag += char print (flag) break
goose 构建challenge镜像
1 docker build challenge -t goose:challenge
然后
1 socat -v tcp-listen:31335,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -p 31336\:8123 -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} -e SERVICE_HOST=10.249.10.107 -e SERVICE_PORT=31336 goose\:challenge"
后面就能通过nc与31335端口交互
LaunchDotCom公司有一颗新的卫星-Carnac2.0。卫星地面站正在与其进行遥测数据接收,遥控指令发送。本挑战题要求根据卫星的设计文档,思考如何获取flag。
使用nc连接到靶机后,显示遥测服务正在发送一系列二进制数据,打印出来是乱码,参赛者需要研究这颗新卫星的设计文档,从中解码出flag值。
solve.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 import bitstringimport osimport sysimport socketimport randomimport timeFLAG_APID = 102 EPS_APID = 103 PAYLOAD_APID = 105 class cmdSender : def __init__ (self, APID ): self .packet_version = 0 self .packet_type = 1 self .sec_header_flag = 0 self .APID = APID self .sequence_flags = 3 self .packet_sequence_count = random.randint(1000 , 10000 ) self .packet_data_length = 1 def sendCMD (self, socket, payload ): self .packet_data_length = len (payload) - 1 packet = bitstring.pack('uint:3, uint:1, uint:1, uint:11, uint:2, uint:14, uint:16' , self .packet_version, self .packet_type, self .sec_header_flag, self .APID, self .sequence_flags, self .packet_sequence_count, self .packet_data_length) packethdr = packet.tobytes() wholepacket = packethdr + payload self .packet_sequence_count += 1 socket.send(wholepacket) return True if __name__ == '__main__' : Host = '10.249.10.107' Port = 31335 print (Host,Port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect((Host, Port)) ticket = os.getenv("TICKET" , "" ) if len (ticket): sock.recv(len ("Ticket please:\n" )) sock.send((ticket+"\n" ).encode('utf-8' )) print ("Sent: " + ticket) line = sock.recv(256 ) sock.close() Host, Port = line.split(b" " )[-1 ].split(b":" ) print (Host,Port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect((Host, int (Port))) time.sleep(1 ) cmd = cmdSender(EPS_APID) time.sleep(1 ) cmd.sendCMD(sock, b'\x00\x02\x01' ) time.sleep(1 ) cmd.sendCMD(sock, b'\x00\x0c\x03\xde' ) while True : data = sock.recv(6 ) s = bitstring.BitArray(data) version, type , sec_header, apid, sequence_flags, sequence_count, data_length = s.unpack('uint:3, uint:1, uint:1, uint:11, uint:2, uint:14, uint:16' ) print ("APID: {}\nLength: {}\n" .format (apid, data_length)) data = sock.recv(data_length+1 ) if apid != FLAG_APID: print ("Ignoring APID we don't care about" ) continue s = bitstring.ConstBitStream(data) char = ' ' flag = '' while char != '}' : char = chr (s.read('uint:7' )) flag += char print (flag) break
通信系统信息安全 phasor 主办方向参赛者提供了一个challenge.wav文件,其内容是一段SDR(Software Defined Radio,软件无线电)捕获的数据,要求参赛者去解调它,并从中找到flag。
对于这一类题型,我们可以使用Universal Radio Hacker(URH)工具来解调。URH工具是一个用于逆向解析和攻击无线通信协议的开源工具,可以对原始采样信号进行解调解码,将收到的信号映射成bit数据,并将bit数据解析成可读性高的文本。
天体测量信息安全 matters_of_state Dockerfile里要把python-dev换为python3-dev
requirements.txt修改为
1 2 3 orbitalpy==0.7.0 numpy represent==1.6.0.post0
先构建docker镜像
1 docker build challenge -t matters_of_state:challenge
然后
1 socat -v tcp-listen:12345,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -e SEED=1465500232115169100 -e FLAG=flag{TESTflag1234} matters_of_state\:challenge"
后面就能通过nc与12345端口交互
challenge.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 import osimport sysimport randomimport orbitalimport numpy as npimport astropy from timeout import timeout,TimeoutErrorto = int ( os.getenv("TIMEOUT" ,120 )) def str_to_vec ( str_in ): vec = np.fromstring( str_in , dtype=float , count=-1 , sep=',' ) if ( vec.size != 3 ): raise "Vector doesnt have 3 elements" return vec def single ( ): pos_tolerance = 10.0 vel_tolerance = 0.1 correct = True print ("Orbital Elements: " ) RE = 6378.0 a = 10.0 * RE e = 0.3 i = 63.0 RAAN = 25.0 peri = 78.0 mu = 398600.5 n = np.sqrt( mu / np.power(a,3 )) M = 10.0 times = ['2022-01-01T00:00:00' ] t = astropy.time.Time(times, format ='isot' , scale='utc' ) orbit = orbital.elements.KeplerianElements( a=a*1000.0 , e=e, i=np.deg2rad(i), raan=np.deg2rad(RAAN) , arg_pe=np.deg2rad(peri), M0=np.deg2rad(M), body=orbital.bodies.earth , ref_epoch=t ) orbit.propagate_anomaly_by(M=0.0 ) pos_truth = orbit.r/1000.0 vel_truth = orbit.v/1000.0 print ("Given the following orbit elements: " ) print ("semi-major axis: {} km" .format (a)) print ("eccentricity: {}" .format (e)) print ("inclination: {} deg" .format (i)) print ("RAAN: {} deg" .format (RAAN)) print ("Mean anomaly: {} deg" .format (M)) print ("Argument of periapsis: {} deg" .format (peri)) print ("Time: {}" .format ( t[0 ] )) print ("Find the state vector of the statellite" ) print ("Position: X,Y,Z " , flush=True ) pos_answer = input ( ) p = str_to_vec( pos_answer ) print ("Velocity: Vx,Vy,Vz" , flush=True ) vel_answer = input ( ) v = str_to_vec( vel_answer ) dP = np.linalg.norm( pos_truth - p ) dV = np.linalg.norm( vel_truth - v ) print ("dP: {} dV: {}" .format ( dP ,dV ), flush=True ) if ( dP > pos_tolerance ): print ("Position incorrect" , flush=True ) correct = False if ( dV > vel_tolerance ): print ("Velocity incorrect" , flush=True ) correct = False return correct @timeout( to ) def main (): N = 5 for k in range ( N ): ok = single( ) if ( False == ok ): print ("Wrong" , flush=True ) print ("....Later" , flush=True ) sys.exit(0 ) print ("Correct" , flush=True ) flag = os.getenv("FLAG" ) print ("Flag: {}" .format ( flag ) , flush=True ) if __name__ == "__main__" : try : main() except TimeoutError: print ("Timeout.....bye" ) sys.exit(0 )
源码分析
给出开普勒轨道要素 与时间 ,让选手在给定公差内返回三维位置/速度 向量(km 和 km/s)。
关键点:
换言之,参赛者只要能把给定六根数按地球二体轨道模型,转换为 ECI 坐标系下的 $\mathbf r,\mathbf v$,并满足阈值,就能通关。
solver.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 import socketimport osimport numpy as npimport sysimport re import sgp4.api as sp4import datetimeimport helperdef get_value ( text , preamble ): lines = text.split("\n" ) out = "" for line in lines: if ( preamble in line ): out = line value = re.findall("\d+\.\d+" , out) return float (value[0 ] ) def get_date ( text ,preamble ): lines = text.split("\n" ) out = "" for line in lines: if ( preamble in line ): out = line.replace(preamble,"" ) out = out.replace("UTC" ,"" ) out = out.strip() out=out+"+0000" date = datetime.datetime.strptime( out , '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S%z' ) return date def mean_to_eccentic ( M , e , tol=1e-5 ): if ( M > np.pi ): M0 = np.pi*2 - M else : M0 = M E_guess = np.arange( 0 , np.pi , tol ) M_Guess = E_guess - e*np.sin(E_guess ) dM =abs ( M0 - M_Guess ) ind = np.argmin( dM , axis=0 ) if ( M > np.pi ): E = 2 *np.pi - E_guess[ind] else : E = E_guess[ind] print ("Eccentric anomaly is: {}" .format ( E)) return E def solve_single ( sock ): print ("Trying to solve" , flush=True ) challenge = sock.read_until(["Find" ,"Flag" ,"Wrong" ]) print (challenge , flush=True ) if ( "Wrong" in challenge): sys.exit(0 ) if ( "Flag" in challenge): print (sock.get_remaining() , flush=True ) sys.exit(0 ) a = get_value( challenge , "semi-major" ) e = get_value( challenge , "eccentricity" ) i = get_value( challenge , "inc" ) RAAN = get_value( challenge , "RAAN" ) peri = get_value(challenge, "Argument" ) M = get_value(challenge, "Mean" ) mu = 398600.4418 inc = np.deg2rad( i ) E = mean_to_eccentic( np.deg2rad(M), e ) TA = np.arccos( (np.cos(E)-e)/(1 - e*np.cos(E))) print ( "True Anomaly is: {}" .format ( TA )) R = np.deg2rad( RAAN ) W = np.deg2rad( peri ) + TA r = a*(1 - e*np.cos(E)) v = np.sqrt( mu * ( (2 /r) - (1 /a) ) ) fpa = np.arctan( e*np.sin(TA ) / (1 + e*np.cos(TA))) if ( TA > np.pi ): fpa = -fpa D1 = np.array( [np.cos(-W), np.sin(-W), 0 , -np.sin(-W), np.cos(-W) , 0 ,0 ,0 , 1 ]) D2 = np.array( [1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , np.cos(-inc) , np.sin(-inc) , 0 , -np.sin(-inc), np.cos(-inc)] ) D3 = np.array( [np.cos(-R), np.sin(-R), 0 , -np.sin(-R), np.cos(-R) , 0 ,0 ,0 , 1 ]) D1 = D1.reshape(3 ,3 ) D2 = D2.reshape(3 ,3 ) D3 = D3.reshape(3 ,3 ) rot = np.matmul( D3, np.matmul( D2, D1 )) rot2 = rot.transpose() print ( "FPA is {}" .format ( fpa)) print ("Velocity is: {}" .format ( v)) v_r = v * np.sin( fpa ) v_w = v * np.cos( fpa ) R_VEC = np.array([r , 0 , 0 ]) V_VEC = np.array([v_r , v_w , 0 ]) R_VEC = R_VEC.reshape(3 ,1 ) V_VEC = V_VEC.reshape(3 ,1 ) print ( V_VEC ) position = np.matmul( rot , R_VEC ).reshape(1 ,3 ) velocity = np.matmul( rot,V_VEC).reshape(1 ,3 ) position = position[0 ] velocity = velocity[0 ] pos = "{},{},{}\n" .format ( position[0 ], position[1 ], position[2 ]) vel = "{},{},{}\n" .format ( velocity[0 ], velocity[1 ], velocity[2 ]) print ("I think the position is: {}" .format ( pos), flush=True ) print ("I think the velocity is: {}" .format ( vel ), flush=True ) sock.send( pos ) sock.send( vel) def batch_solve (host, port ): s = helper.TcpReader( host, port ) ticket = os.getenv("CHAL_TICKET" ) if ( ticket != None ): s.read_until("Ticket please:" ) print ("Sending ticket - {}" .format ( ticket ), flush=True ) s.send( ticket) s.send( "\n" ) ticket_sent = True keep_going = True while ( keep_going ): solve_single(s) if __name__ == "__main__" : host = '10.249.10.107' port = 12345 batch_solve( host , port )
解题脚本流程:
从环境变量获取连接参数:CHAL_HOST、CHAL_PORT。若有工单/凭证 CHAL_TICKET,先按服务端提示发送。
轮询读取服务端的挑战文本,判断三种情形:
含 Wrong:退出(上一轮答错)
含 Flag:读取并打印剩余内容,退出(通关)
含 Find:这是题面,进入求解。
解析题面中的数值:semi-major、eccentricity、inc(倾角)、RAAN、Argument(近地点幅角)、Mean(平近点角)。
以标准地球引力常数 $\mu=398600.4418,\text{km}^3/\text{s}^2$ 进行二体问题 求解:
$M\to E$(平近点角到偏近点角)
$E\to \nu$(偏近点角到真近点角)
$a,e,\nu\to r,v$(轨道半径与速度模长)
计算飞行路径角 $\gamma$(Flight Path Angle, FPA),把 (v) 分解为径向与切向分量 $v_r,v_t$
用旋转矩阵把**轨道平面坐标系(PQW/Perifocal)**矢量转到 ECI
把得到的 position、velocity 以 “逗号分隔+换行” 的格式回发。
数学推导与公式说明
轨道六根数回顾
给定地球二体模型下的六根数:
Kepler 方程:求偏近点角 $E$
Kepler 方程(椭圆轨道):mean_to_eccentic(M,e,tol) 用网格枚举在 $[0,\pi]$ 以 tol 为步长近似求解,并对 $M>\pi$ 做对称处理。虽然不如牛顿法精确高效,但在该题误差阈值下通常足够。
偏近点角 $E$ 到真近点角 $\nu$
脚本采用:atan2:atan2 能自动处理象限。
轨道半径 $r$ 与速度模长 $v$
轨道半径(椭圆几何关系):
由 Vis-Viva 方程 得速度模长:
飞行路径角 $\gamma$ 与速度分解
脚本用:
坐标系与旋转(PQW → ECI)
PQW/Perifocal (轨道平面)坐标系:ECI :惯性坐标系(地球赤道春分点为参考)。
标准从 PQW 到 ECI 的方向余弦矩阵(DCM)是:
脚本做了一个等效 变换:先把真近点角 $\nu$ 并入到第一步旋转D1,D2,D3 正是这三步的矩阵展开。
小结:位置 在 PQW 中位于 $x$ 轴(近地点方向),速度 在 PQW 中由 $(v_r,v_t,0)$ 表示,随后一次旋转到 ECI。
脚本实现细节与注意事项
文本解析(get_value,get_date)
get_value(text, preamble):逐行寻找包含关键前缀的行,用正则 \d+\.\d+ 抓取第一个小数 并转为 float。
局限:不支持整数 (如 10 没有小数点)、负数、科学计数法;若行里有多个数字,它只取第一个。
但题面格式固定、均为小数形式,因此能用。
get_date 未使用(被注释掉),题面给的时间只作为展示,脚本假定当前历元即题面时间,因此不做传播。
Kepler 方程求解(mean_to_eccentic)
采用网格搜索 (步长 tol),并用对称性把 $[0,2\pi)$ 的问题折半到 $[0,\pi]$。
精度由 tol 控制;容差适当即可满足误差阈值。
姿态旋转矩阵构造
构造 D1=R3(-W)、D2=R1(-i)、D3=R3(-Ω),并按 rot = D3 @ (D2 @ D1) 相乘(从右到左依次作用)。
然后 r=rot @ [r,0,0]^T,v=rot @ [v_r,v_t,0]^T,得到 ECI 坐标。
解题思路
读题面 → 解析六根数 求 $E$ :解 $M=E-e\sin E$求 $\nu$ :由 $E$ 得到真近点角求 $r,v$ :$r=a(1-e\cos E)$,$v=\sqrt{\mu(2/r-1/a)}$分解速度 :$(v_r,v_t)=(v\sin\gamma,,v\cos\gamma)$ 或直接用 $\sqrt{\mu/p}$ 公式坐标变换 :$\mathbf r=\mathbf{rot}[r,0,0]^T$,$\mathbf v=\mathbf{rot}[v_r,v_t,0]^T$,其中按协议回填 :格式 x,y,z\n 与 vx,vy,vz\n循环处理直至拿到 Flag
其他太空信息安全挑战 mission 构建challenge镜像
1 docker build challenge -t mission:challenge
然后
1 socat -v tcp-listen:31344,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} mission\:challenge"
后面就能通过nc与31344端口交互
这是一道关于侦察卫星的挑战题,在给定的背景下,要求制订该卫星的任务规划,实现拍摄并下传特定目标的目的。
用nc连接靶机后会获取很长一段提示信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 ########################## Mission Planning Challenge ########################## 给出了当前时刻 The current time is April 22, 2020 at midnight (2020-04-22T00:00:00Z). 给出了侦察目标(伊朗航天港) We need to obtain images of the Iranian space port (35.234722 N 53.920833 E) with our satellite within the next 48 hours. 要求设计一个计划用来对目标拍照,同时下传照片 You must design a mission plan that obtains the images and downloads them within the time frame without causing any system failures on the spacecraft, or putting it at risk of continuing operations. 给出了侦察卫星的TLE The spacecraft in question is USA 224 in the NORAD database with the following TLE: 1 37348U 11002A 20053.50800700 .00010600 00000-0 95354-4 0 09 2 37348 97.9000 166.7120 0540467 271.5258 235.8003 14.76330431 04 The TLE and all locations are already known by the simulator, and are provided for your information only. Requirements ############ 给出了要求的照片大小及接收照片的地面站(美国阿拉斯加州费尔班克斯地面站)的坐标 You need to obtain 120 MB of image data of the target location and downlink it to our ground station in Fairbanks, AK (64.977488 N 147.510697 W). 要求给出48h的卫星任务规划 Your mission will begin at 2020-04-22T00:00:00Z and last 48 hours. You are submitting a mission plan to a simulator that will ensure the mission plan will not put the spacecraft at risk, and will accomplish the desired objectives.
(2)任务规划格式:每行是一个任务,格式是日期+时间+模式,其中由于模拟器的原因,时间中的“秒”总是为0.卫星平台有以下4种模式。
sun_point:太阳能帆板对准太阳,开始充电。
imaging:拍照。
data_downlink:下传照片。
wheel_desaturate:轮去饱和,即使用机载磁传感器使航天器反作用轮去饱和,其中反作用轮用于控制卫星姿态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Mission Plan ############ Enter the mission plan into the interface, where each line corresponds to an entry. You can copy/paste multiple lines at once into the interface. 给出了规划的格式,因为模拟器每分钟执行一次,所以时间种的“秒”总是为0 The simulation runs once per minute, so all entries must have 00 for the seconds field. Each line must be a timestamp followed by the mode with the format: 2020-04-22T00:00:00Z sun_point YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:00Z next_mode ... 要注意确保平台在此期间是可用的 The mission will run for it's full duration, regardless of when the image data if obtained. You must ensure the bus survives the entire duration. Mode Information ################ 平台有4种模式 The bus has 4 possible modes: - sun_point: Charges the batteries by pointing the panels at the sun. - imaging: Trains the imager on the target location and begins capturing image data. - data_downlink: Slews the spacecraft to point it's high bandwidth downlink transmitter at the ground station and transmits data to the station. - wheel_desaturate: Desaturates the spacecraft reaction wheels using the on board magnetorquers. Each mode dictates the entire state of the spacecraft. The required inputs for each mode are already known by the mission planner.
(3)卫星平台信息
星载计算机有95MB存储空间,也就是说要拍两次以上才能满足120MB的要求。
所有组件有效工作温度是0-60摄氏度。
反作用轮的最大速度是7000RPM。
在任务执行过程种每分钟会收到一组遥测信息。
需要依据遥测信息不断调整模式,确保卫星平台始终可用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Bus Information ############### The onboard computer has 95 MB of storage. All bus components are rated to operate effectively between 0 and 60 degrees Celsius. The battery cannot fall below 10% capacity, or it will reduce the life of the spacecraft. The reaction wheels have a maximum speed of 7000 RPM. You will received telemetry from the spacecraft throughout the simulated mission duration. You will need to monitor this telemetry to derive the behavior of each mode. ########################################################################
(4)对参赛者输入的要求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Please input mission plan in order by time. Each line must be a timestamp followed by the mode with the format: YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ssZ new_mode Usage: run -- Starts simulation plan -- Lists current plan entries exit -- Exits Once your plan is executed, it will not be saved, so make note of your plan elsewhere.
构建solver环境
1 docker build solver -t mission:solver
测试
1 2 3 socat -v tcp-listen:31344,reuseaddr exec:"docker run --rm -i -e SEED=1234 -e FLAG=flag{1234} mission\:challenge" docker run --rm -e HOST=172.17.0.1 -e PORT=31344 mission:solver
 `
`